→ ACCES ←
Données climatiques annuelles et mensuelles (et altitude) pour tous les points du monde.
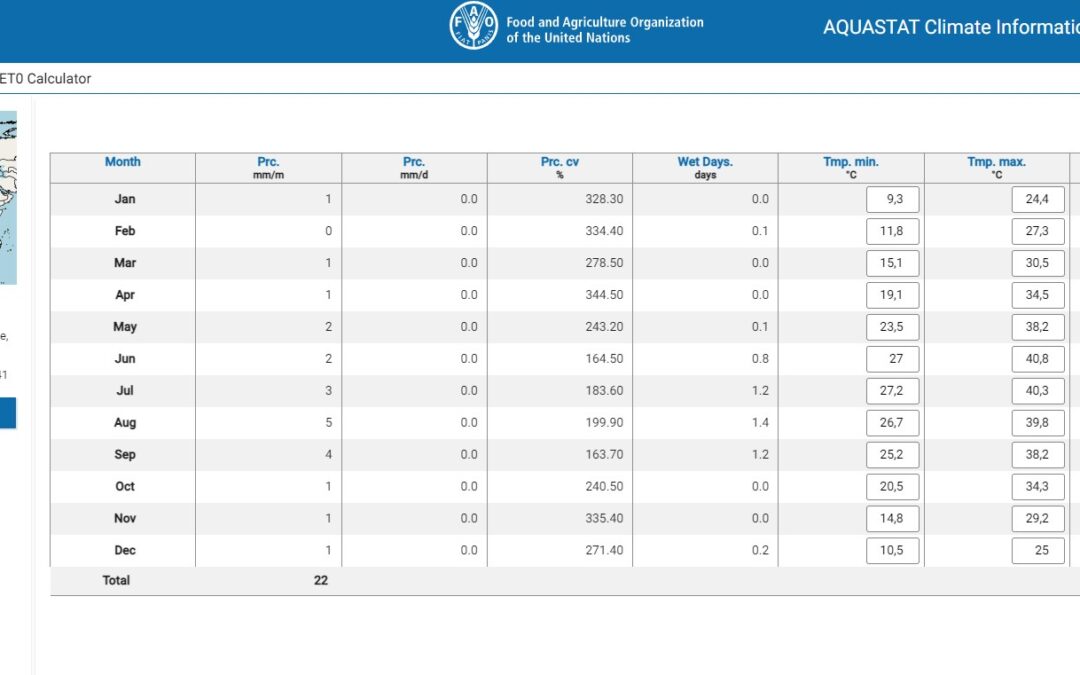
The Climate Information Tool is an interactive tool to query a spatial dataset containing long-term mean monthly climate data.
The dataset covers the global land surface at a 10 minute spatial resolution for the period 1961-1990. The tool displays the latitude, longitude and elevation of the chosen location, and several climate variables per month (average over the period 1961-1990) related to: precipitation, temperature, relative humidity, sunshine, wind speed, reference evapotranspiration. In more details the tool displays:
- Precipitation in mm/month
- Precipitation in mm/day
- Coefficient of Variation of precipitation in percentage
- Wet days
- Mean temperature in °C
- Maximum temperature in °C
- Minimum temperature in °C
- Days of groundfrost
- Relative humidity in percentage
- Sunshine fraction in percentage
- Wind speed at 2 metre above the surface in m/sec
- Reference evapotranspiration in mm/month
- Reference evapotranspiration in mm/day
All data, apart from the reference evapotranspiration, originate from the CRU CL 2.0 data-set which is described in: New, M., Lister, D., Hulme, M. and Makin, I., 2002: A high-resolution data set of surface climate over global land areas. Climate Research 21:1-25. The data are available through the School of Geography Oxford, the International Water Management Institute World Water and Climate Atlas and the Climatic Research Unit of the University of East Anglia.
The wind speed listed in the CRU CL 2.0 data-set is expressed in m/s at 10 metres above the surface. For agrometeorological applications it is better to express the wind speed at 2 metres above the surface. Therefore, the wind speed values have been adjusted using the methodology described in FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56, Crop Evapotranspiration – Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. The same publication is used to calculate reference evapotranspiration.
The data available in the data-set refer to mean circumstances that are obtained by interpolating data from different climate stations. The data give an indication of climatic conditions but can never replace data obtained through stations. For more accurate assessments, it is therefore advisable to use as much as possible locally measured climate data.